Description
YM Fast SEO enhances your website with powerful, intuitive, and user-friendly SEO tools. In today’s digital world, SEO is essential for driving organic traffic and improving your website’s visibility on search engines.
With YM Fast SEO, you can easily manage important aspects of search optimization without unnecessary complexity. Unlike bulky alternatives, this lightweight plugin is efficient, flexible, and easy to extend, allowing you to keep full control over your website’s performance.
Features
- Lightweight & Extendable
- Meta Tag Fields for Posts and Taxonomies
- Automated Open Graph, Twitter Card, and Schema.org Markups
- AI Crawlers Support
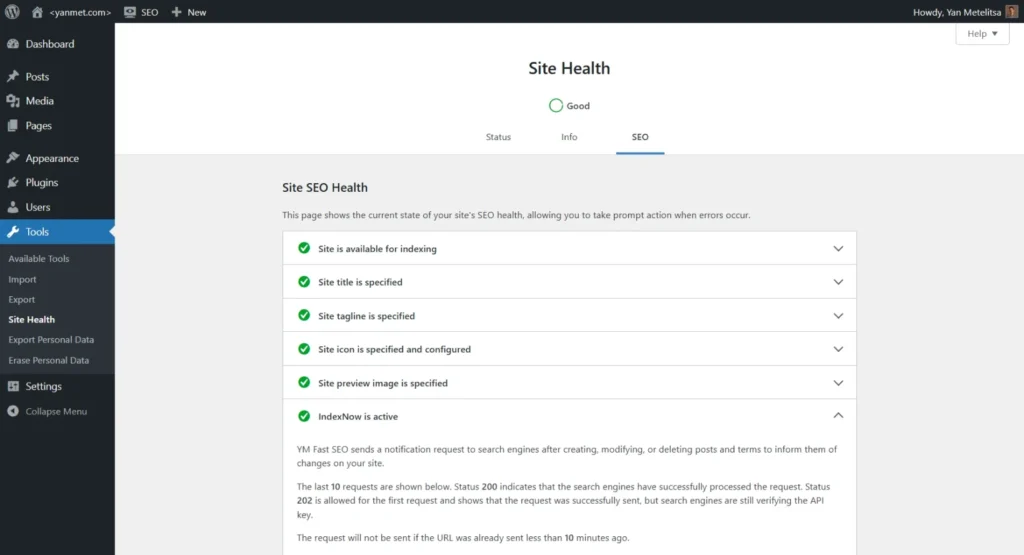
- Automatic IndexNow Sending
- Quick SEO Analysis and Site SEO Health Page
- Services Integration (Analytics + Webmasters)
- SVG Favicon Support
Robots.txtEditor- Other Useful Tools & Improvements
Screenshots
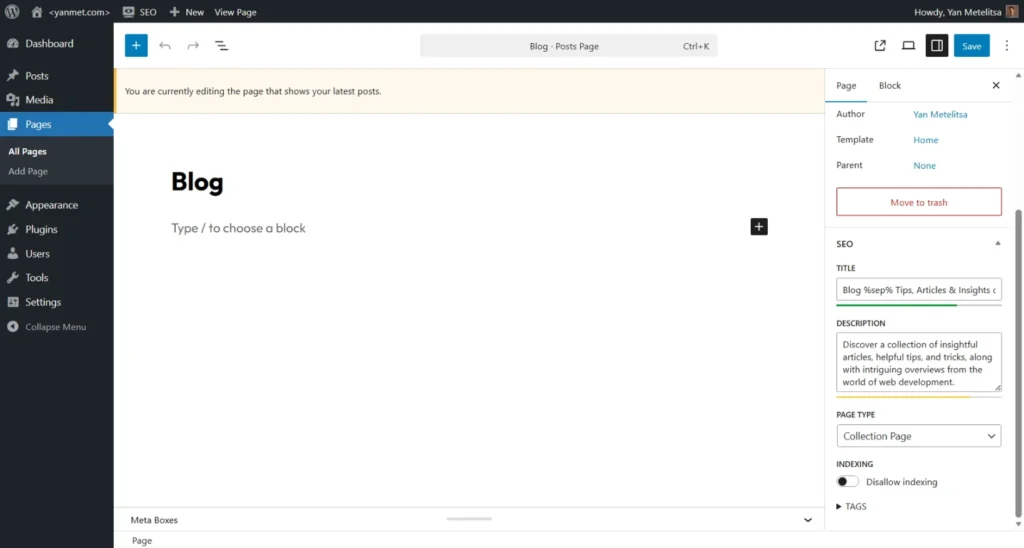
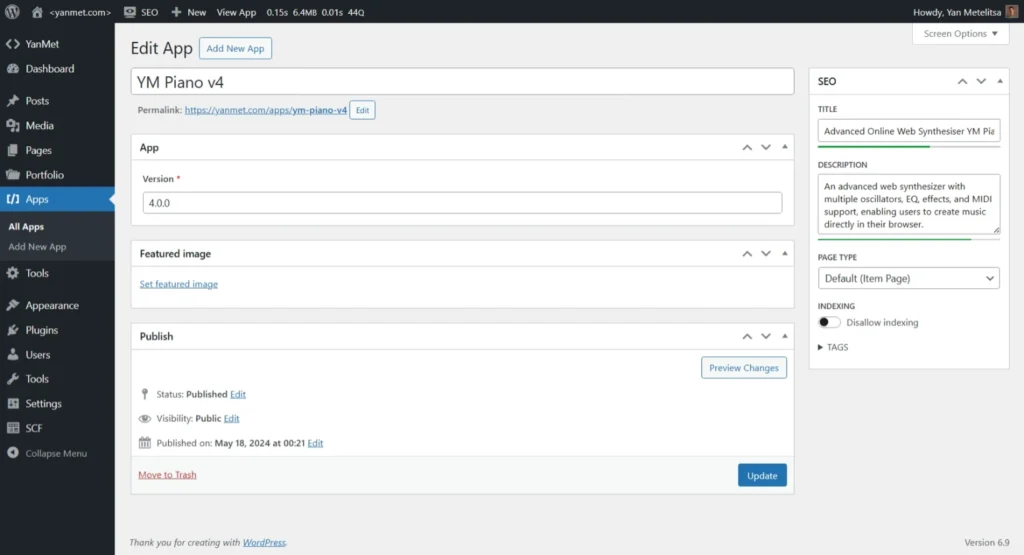
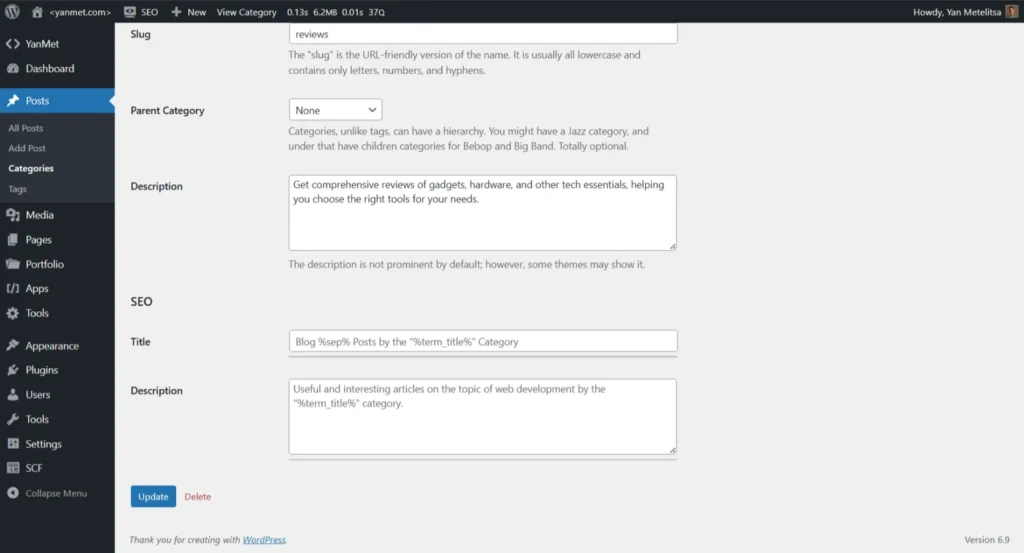
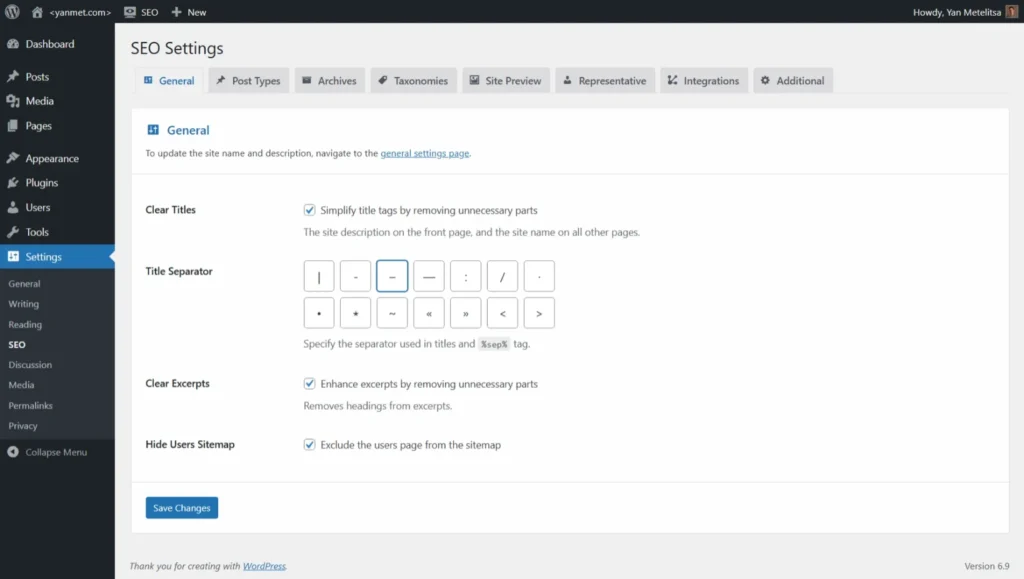
Extensibility
In addition to the powerful features mentioned above, YM Fast SEO is designed for extensibility. You can easily enhance and customize its functionality to suit your specific needs using the hooks provided. The following actions and filters allow you to add your own meta tags, modify existing meta fields, and integrate additional functionalities, making it easy to adapt the plugin to your unique requirements.
By leveraging these hooks, you can ensure that YM Fast SEO grows with your website, providing you with the flexibility and control necessary for optimal performance.
Actions
ymfseo_after_print_metas
If you need to print specific meta tags or any other content in the <head> section, you can use the ymfseo_after_print_metas hook. Simply write the necessary output in its callback function, and the elements will be displayed at the end of the YM Fast SEO output.
// Prints additional meta tags. add_action( 'ymfseo_after_print_metas', function () { echo '<meta name="twitter:domain" content="yanmet.com">'; });
Filters
ymfseo_title_separator
If none of the separators offered in the settings suit you, you can set a custom value using this filter.
/** * Modifies YM Fast SEO separator symbol. * * @param string $sep Separator symbol. * * @return string */ add_filter( 'ymfseo_title_separator', function ( string $sep ) : string { $sep = '<>'; return $sep; });
ymfseo_print_head_scripts
If you need advanced head scripts display logic, you can use this filter.
/** * Determines whether YM Fast SEO head scripts will be printed. * * @param bool $should_print Initial value. * @param bool $only_visitors "Only for Visitors" option value. * * @return bool */ add_filter( 'ymfseo_print_head_scripts', function ( bool $should_print, bool $only_visitors ) : bool { // Custom logic. return $should_print; });
ymfseo_tags
If you want to add custom tags to use in meta fields, you can use the following filters:
/** * Modifies YM Fast SEO replace tags list. * * @param array $tags Replace tags list. * * @return array */ add_filter( 'ymfseo_tags', function ( array $tags ) : array { $tags = array_merge( $tags, [ '%my_tag%' => 'My replace string', ]); return $tags; });
ymfseo_{$post_type}_posts_tags
/** * Adds custom tags for Product post type. * * @param array $tags Post type replace tags. * @param int $post_id Post ID. * * @return array */ add_filter( 'ymfseo_product_posts_tags', function ( array $tags, int $post_id ) : array { $tags = [ '%quantity%' => '', ]; if ( $post_id ) { $product = wc_get_product( $post_id ); $tags[ '%quantity%' ] = $product->get_stock_quantity(); } return $tags; }, 10, 2 );
ymfseo_{$taxonomy}_taxonomy_tags
/** * Adds custom tags for Product Category taxonomy terms. * * @param array $tags Taxonomy replace tags. * @param int $term_id Term ID. * * @return array */ add_filter( 'ymfseo_product_cat_taxonomy_tags', function ( array $tags, int $term_id ) : array { $tags = [ '%my_field%' => '', ]; if ( $term_id ) { $tags[ '%my_field%' ] = get_field( 'my_field', "term_{$term_id}" ); } return $tags; }, 10, 2 );
ymfseo_meta_fields
You can also modify the raw data values, which are later used to generate basic meta tags and other elements.
The ymfseo_meta_fields filter passes an associative array that you can modify by applying your own logic. It’s crucial to perform a type check on the query object before making changes, as the same ID might be associated with different post records or taxonomy terms.
/** * Modifies YM Fast SEO meta fields. * * @param array $meta_fields Meta fields array. * @param WP_Post|WP_Post_Type|WP_Term|WP_User|null $queried_object Queried object. * * @return array */ add_filter( 'ymfseo_meta_fields', function ( array $meta_fields, $queried_object ) : array { // Exits if `$queried_object` is null. if ( is_null( $queried_object ) ) { return $meta_fields; } // `$queried_object` may be of `WP_Post`, `WP_Post_Type`, `WP_Term`, and `WP_User` class. switch ( get_class( $queried_object ) ) { case 'WP_Post': switch ( $queried_object->post_type ) { // Sets ACF/SCF field value as default meta description for product post type. case 'product': if ( empty( $meta_fields[ 'description' ] ) ) { $meta_fields[ 'description' ] = get_field( 'description', $queried_object->ID ); } break; } break; case 'WP_Post_Type': switch ( $queried_object->name) { // Sets custom page fields as fields for archive product page. case 'product': $product_acrhive_page_post = get_post( wc_get_page_id( 'shop' ) ); $product_acrhive_page_fields = new YMFSEO_Meta_Fields( $product_acrhive_page_post ); $meta_fields = (array) $product_acrhive_page_fields; break; } break; } return $meta_fields; }, 10, 2 );
ymfseo_schema_org
The ymfseo_schema_org filter is applied to modify or add new Schema.org entities and parameters.
/** * Modifies Schema.org JSON-LD. * * @param array $schema_org Schema.org data array. * @param WP_Post|WP_Post_Type|WP_Term|WP_User|null $queried_object Queried object. * * @return array */ add_filter( 'ymfseo_schema_org', function ( array $schema_org, $queried_object ) : array { // Exits if `$queried_object` is null. if ( is_null( $queried_object ) ) { return $schema_org; } // Modificate here. return $schema_org; }, 10, 2 );
ymfseo_{$post_type}_posts_llms_txt_custom_fields
Is used to append custom fields to the llms-full.txt output for a specific post type.
/** * Adds custom fields to `llms-full.txt` output for Products. * * @param string[] $fields Fields array. * @param int $post_id Post ID. * * @return array */ add_filter( 'ymfseo_product_posts_llms_txt_custom_fields', function ( array $fields, int $post_id ) : array { $product = wc_get_product( $post_id ); $fields = [ 'Price' => $product->get_price(), ]; return $fields; }, 10, 2 );

